Utilizing the printing method for packaging depends on several factors. With a greater understanding of the different types, you can select the most suitable option for your requirements. In this article, we assess the many printing methods for packaging. Moreover, their pros and cons and what kind of ink they use will be discussed.
Different Types of Printing Methods for Packaging
Comparing and contrasting the different package printing methods appropriate for your product is integral to the packaging redesign procedure. Diverse end-use applications are compatible with the many printing methods that are currently available. Let’s dive into the various types of printing for packaging.
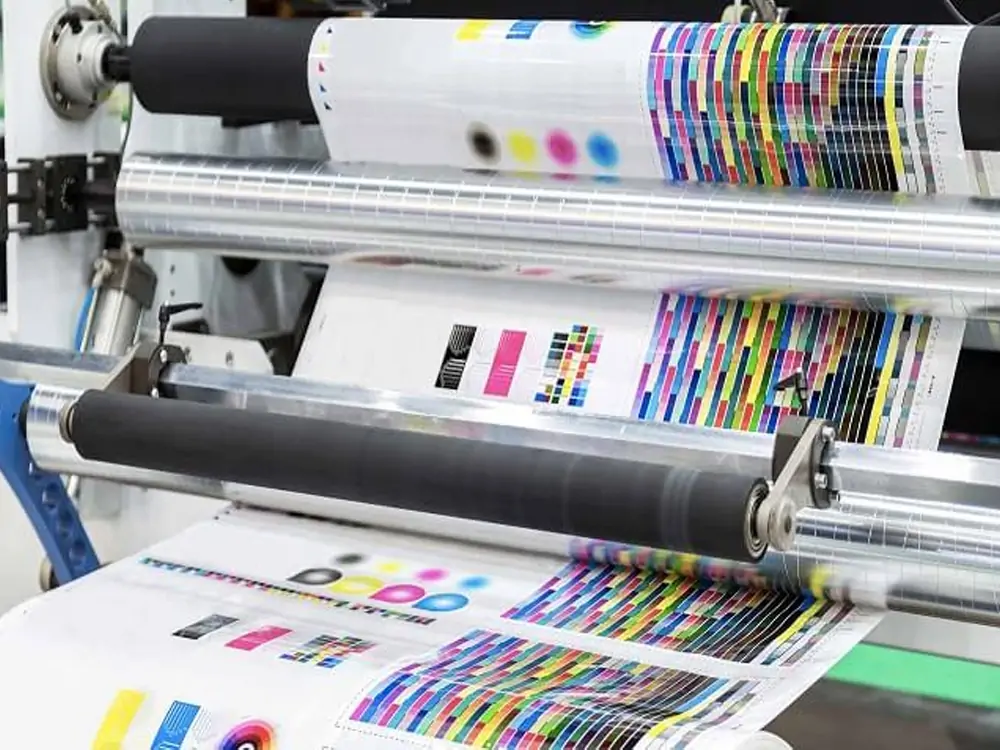
1. Offset Lithography
Offset lithographic printing is also known as offset printing. It produces high-quality, large-volume prints using the traditional method. Large or flat items, including corrugated packaging and folding cartons. Furthermore, offset lithography often has large labels on packaging and retail displays.
The aluminum plate receives the imprint. It sends it to a rubber blanket for lithographic processing. After printing, place the image on a surface. You can protect and enhance this surface with varnish or coating.

Pros
Before you select this printing method for the packaging of bulk products, consider the following lithography benefits.
- The four-color printing system is often used.
- Boxes for retail products such as electronics, food, and cosmetics are ideal for printing.
- Provides superior printing quality
- Distinctive coatings like matte and glossy finishes are applied to the packaging. It enhances its aesthetic appeal.
- Incorporated two PMS colors into a set of four
- Graphics feature color gradients that are uniform and seamless.
Cons
- It is only compatible with oil-based inks. These solvent-based produce significant quantities of volatile organic compounds.
- More waste is produced during setup. A manufacturer must run several units through the machine. They do this before the print quality reaches a suitable standard. It increases with the number of colors.
- Suitable only for malleable, lightweight substances such as paperboard and paper
- The complex setup means costs for small volumes and MOQs are higher.
Inks for Lithography Ink Packaging
A surface is treated with nitric acid and gum Arabic solution for printing. The image zone is grease-responsive, while non-printing areas are water-receptive. However, this does not affect the outer printing layer. It remains wet due to applying oil-based pigment onto the surface using a charged roller.
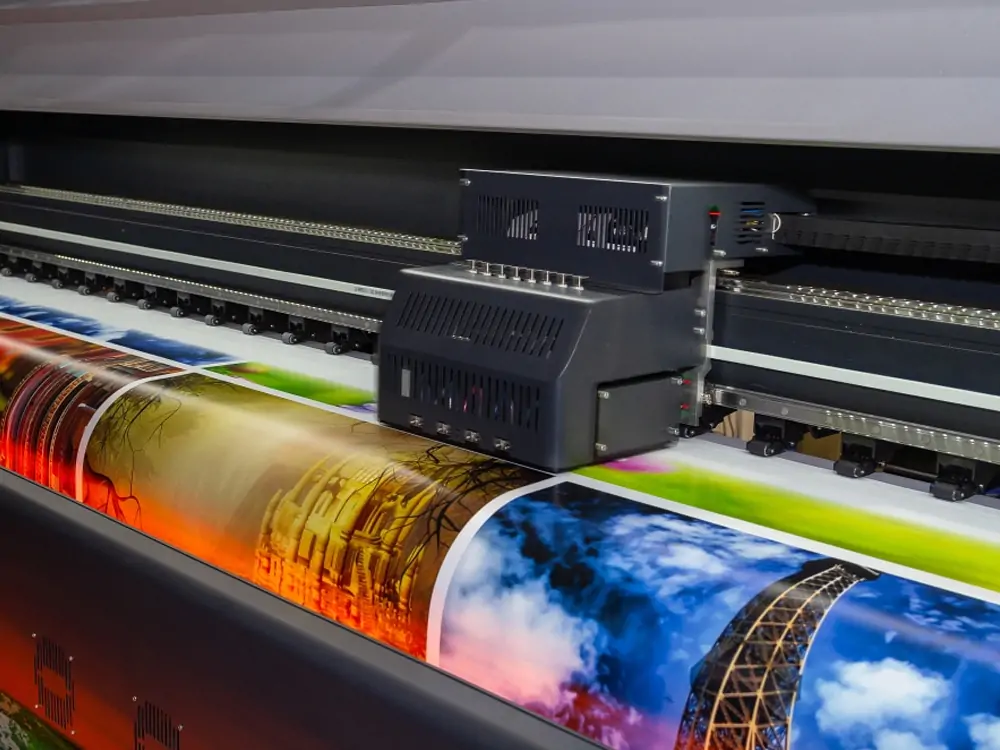
2. Digital Printing
Digital printing is a popular technique for use in product packaging. Digital printing, in contrast to offset, flexo, and gravure, is a relatively recent technology. This direct printing method uses a digital laser or ink-jet printer. It imprints the desired information directly onto the packaging.
Digital printing is an economical choice for small print runs because of the absence of the need for a mechanical setup. Furthermore, it has full-color printing (CMYK) capability. It provides you with unparalleled versatility when it comes to designing artwork. And because everything is digital, last-minute adjustments to the artwork are easy to make.
This printing method is most effective for flexible packaging. It is used in corrugated and folding cartons when applied to film.

Pros
Listed below are some advantages of digital printing methods for packaging.
- Provides a low minimum
- Needs slight to no investment in manufacturing in contrast to lithography.
- Limited-run and compact format
- Print and deliver promptly to the customer’s doorstep
Cons
- Incapable of employing metallic pigments and luster
- Minimal coating protection is necessary.
- Difficulty in coordinating PMS colors
- The cost per unit is excessively costly.
- Do not provide an excessive number of coating options in comparison to litho.
- Digital printing incurs a more significant expense than alternative methods when applied to orders of considerable volume.
3. Flexography
Flexo printing is another term for flexographic printing. This technique prints on plastic, paper, and other materials. Cylinders roll around flexible plates to do the printing. You can personalize these plates with your artwork and spin them quickly by printing directly on the packaging.
Flexography has improved over the years with increased automation and quality. Users say it can now compete with offset in terms of high-quality printing.
Pros
- Both oil and water ink toners were utilized.
- Demand the least amount of tooling in comparison to offset.
- Comparatively affordable price.
Cons
- Failure to ensure a seamless color change during printing may lead to printing issues.
- It has slightly lower printing quality when compared to Litho.
- Unable to deliver a convincing duplicate of the image quality.
Best Inks for Flexography Printing
- Water-based ink
Water-based inks are composed of pigment and water. It adds various substances, such as defoamers and agents, that aid in adhesion and drying.
- Oil-based Ink
Oil-based Inks comprise pigments and hydrocarbons used for printing designs onto the surface. It contains soy oil and mineral oil in substantial amounts.
- Electrum beam and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet and electromagnetic (UV and EM) inks comprise pigments, photoinitiators, monomers, and polymers. These inks are widely used in the food packaging industry for circumferential material deformation.
- Solvent-based ink
Ink derived from solvents consists of alcohols and acetates. Typical starting ratios comprised 10%-20% acetates and 80%-90% alcohols for coloring. Utilize solvent inks when imprinting plastic buying bags.
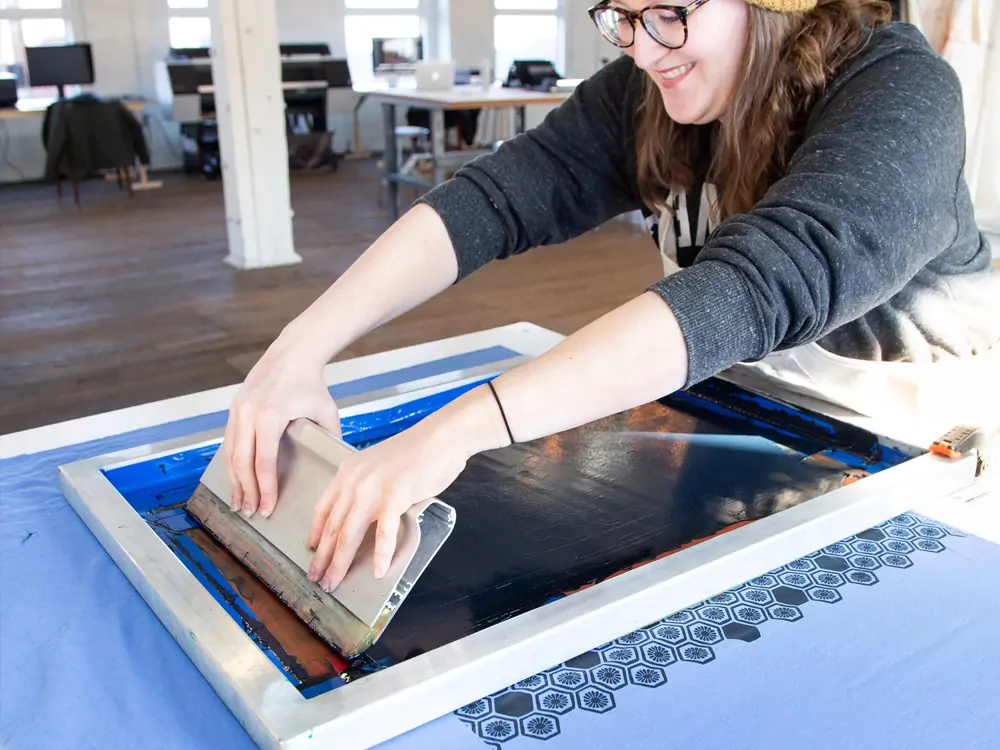
4. Screen Printing
Screen printing is commonly called silkscreen. It consists of an image design and ink passing through a screen; serigraphy is a form of stenciling. The stenciled fragment deposited ink on the opposite side to fabricate the image.
This inking procedure is compatible with various materials. It includes paper, fabric, metal, and glass because the printing surfaces need not be planar.
This printing method packaging is an excellent choice for businesses. It is effective for companies that use stock or prefabricated packaging. You can print promotional and marketing materials on them, including t-shirts and flasks. It is best for labels, promotional materials, and folding cartons.

Pros
- Excellent printing for use on prefabricated packaging and promotional items
- Printing tool setups are inexpensive
- Applicable to lesser quantities of box printing.
- Unlike offset and litho printing, it does not need a flat surface.
Cons
- Delay in the production of your printed goods compared to alternative printing methods
- Not ensure impeccable finishing and cleanness.
- Silk printing is not a viable option for mass production because it cannot reproduce images in photo quality.
- Possibility of human error and abandonment during production.
Best Inks for Screen Printing
Plastisol ink, discharge, expanding ink, and water-based suede inks are used for silkscreens. People are concerned with protecting the environment through PVC and phthalate ink toners.
5. Gravure
In industrial productions of millions of units, rotogravure printing is often used to make a lot of packaging. It is commonly used for printing on folding cartons and elastic stand-up pouches.
Gravure printing cuts out your image from metal tubes. The printing machine adds color from one cylinder to another to create a decent picture. Food products use it for flexible packaging and favor it for intricate package designs.
It could be an ideal printing option. Mainly, the company requires absolute quality printing for its packaging.
Pros
- The product features images and packaging of the highest quality.
- Print your photographic images instantaneously and using rotogravure.
- Printing cylinders have been utilized for decades.
- Adding a four-color process to PMS colors is straightforward and comparable to litho.
- Enable high-volume printing while maintaining exceptional image quality.
Cons
- Significant expenses on tooling.
- Require extended lead periods.
- The coating option is not inherent to this printing method.
Factors Considering the Selection of A Printing Method for Particular Projects
1. Consultation with expert printers to determine the optimal printing technique
Getting information from reputable printers is vital. If you’re starting, you should know about different printing methods for your project. Experts have abundant knowledge about the subject matter. Therefore, an expert print is significant.
The expert will help you choose the best technique based on your:
- project details
- budget
- desired outcome.
2. Understanding the functionalities, limits, and cost-effectiveness of each method
The capabilities and limitations of various techniques vary. To succeed in a project, it’s crucial to grasp the workings and technologies to complete tasks.
Offset lithography is a traditional printing method. It doesn’t need printing plates on a flat surface instead of digital printing. Despite its reliance on metal plates, offset printing remains a practical technique for producing fine art imitations.
Furthermore, screen printing, letterpress, offset printing, and gravure printing have restricted material compatibility. Digital printing is fast, cheap, and can print on many materials. Ideal for large orders and efficiently completes tasks.
Final Words
Every printing method is well-suited to a particular set of design specifications. Flexographic printing is ideal for transit packaging. It possesses basic, striking designs, such as delivery crates. Digital printing makes it easy to create smaller quantities of packaging rapidly. Offset printing is the most optimal selection for packaging. It needs intricate and superior printing.
Flexographic printing is most effective when applied to lesser product quantities. It helps to minimize carbon emissions. Furthermore, more oversized products exhibit enhanced performance when printed using offset methods.
